Magnetic Field Expulsion in Optically Driven YBa2Cu3O6.48
Introduction
YBa2Cu3O6.48 is a high-temperature superconductor known for its unique properties, one of which is magnetic field expulsion. When this material is exposed to light, it exhibits interesting behavior in terms of its magnetic response. This article explores the phenomenon of magnetic field expulsion in optically driven YBa2Cu3O6.48.
Understanding Magnetic Field Expulsion
Superconductors, when cooled below a certain critical temperature, exhibit zero electrical resistance and expel magnetic fields from their interior. This expulsion of magnetic fields is due to the Meissner effect, which is a fundamental property of superconductors. YBa2Cu3O6.48 is a type-II superconductor, which means it allows some magnetic flux to penetrate its interior in the form of vortices.
Optical Excitation and Magnetic Field Behavior
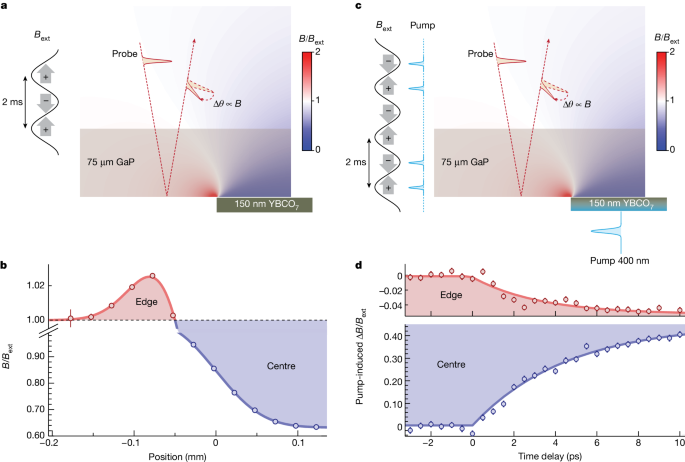
Recent research has shown that when YBa2Cu3O6.48 is exposed to light, its magnetic response is altered. The optical excitation of the material leads to changes in the distribution and density of vortices, affecting the expulsion of magnetic fields. This phenomenon has been studied using various experimental techniques, such as magneto-optical imaging and scanning tunneling microscopy.
Applications
The understanding of magnetic field expulsion in optically driven YBa2Cu3O6.48 has potential applications in the development of advanced superconducting devices. By controlling the magnetic response of the material through optical manipulation, researchers can explore new possibilities for high-temperature superconducting technology.
Conclusion
The study of magnetic field expulsion in optically driven YBa2Cu3O6.48 opens up new avenues for research in the field of superconductivity. By harnessing the interaction between light and superconducting materials, scientists can unravel the complex behavior of these materials and pave the way for innovative technologies. Further studies are needed to fully understand the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon and explore its practical applications.
FAQs
What is YBa2Cu3O6.48?
YBa2Cu3O6.48 is a high-temperature superconductor composed of yttrium, barium, copper, and oxygen. It exhibits unique superconducting properties, such as magnetic field expulsion.
What is magnetic field expulsion?
Magnetic field expulsion is the phenomenon where a superconductor repels magnetic fields from its interior when cooled below a critical temperature. This is known as the Meissner effect.
How does optical excitation affect magnetic field expulsion in YBa2Cu3O6.48?
Optical excitation leads to changes in the distribution and density of vortices in YBa2Cu3O6.48, impacting the expulsion of magnetic fields from the material.